Background
Aerogels, discovered in the late 1930s by chemist Samuel S. Kistler, are fascinating materials known for their light, airy, and translucent appearance and are considered one of the finest insulation materials available today. Aerogels have pores in the range of less than 100 nm in diameter. This morphology results in an ultra-low-density (about 0.0011 to 0.2 g cm-3) and high-porosity solid material. Due to this property, aerogels are also known as “frozen smoke” or “solid air”. More typically aerogel density falls in the range of 0.020 g cm-3 or higher. Because aerogel is mostly air (1-3% of solid content), an excellent thermal insulator is contained within its porous network which presents an effective thermal barrier. The presence of air within their microstructure also makes aerogels excellent sound insulating materials.
The word aerogel refers to the fact that it is derived from gels – effectively the solid structure of a wet gel, only with a gas or vacuum in its pores, instead of liquid. The process of creating an aerogel involves turning a gel, which contains a liquid and solid network, into a solid by replacing the liquid with air through supercritical drying. Aerogels can be made from a wide variety of substances, including silica (SiO2), organic polymers (such as resorcinol-formaldehyde, polyacrylates, polystyrene, polyurethanes, and epoxies), metal oxides (for example, iron oxide and tin oxide), carbon nanotubes, or metals (such as copper and gold).
In their early stages of development silica aerogels were very fragile, but subsequent research and technological advancements led to the development of polymer reinforced aerogels which are mechanically stronger and possess same insulation properties as typical aerogels. Fully polymer based aerogels, which are extremely strong and flexible, have also been formulated. This type of aerogels can be formed into a flexible thin film too.
Aerogels in Flame Retardant Textiles
Aerogels’ thermal conductivity (0.004 to 0.021 W m-1 K-1) is lower than that of air (0.024 to 0.026 W m-1 K-1) at standard atmospheric conditions, thus making them capable of providing a highly efficient thermal insulation at a very low weight. Most research focuses on the application of aerogels in firefighting clothing, extreme environments such as space suits, wetsuits, and footwear products, where insulation against temperature extremes is vital.
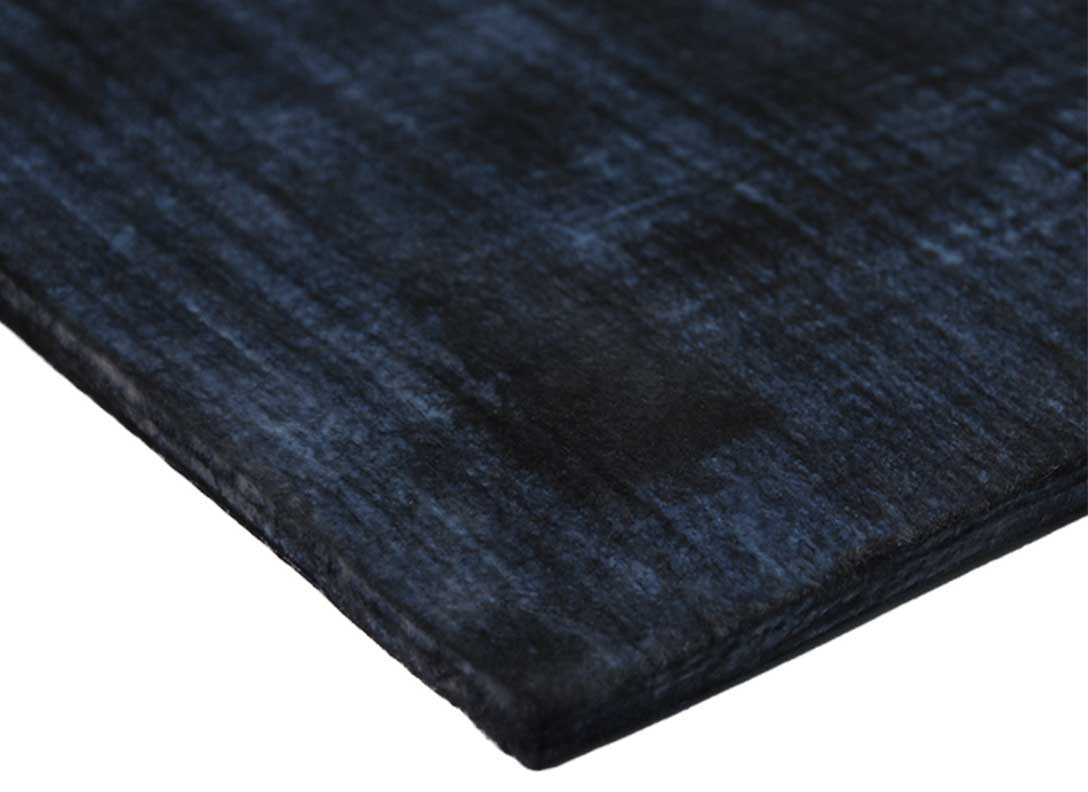

Silica aerogel has unique insulating abilities and been successfully used in many commercial products. Aerogels have been combined with batting to create insulating blankets. Thick blankets of aerogel suspended in a fabric structure have been long used as insulation in the aerospace industry. Aerogels can also be employed to provide flame-retardant finishes to fabrics, such as by coating protective clothing with aerogels. In 2016, Chunxin conducted a study on aerogel-based fire protective clothing, examining the insulation material and performance of active fire protective clothing. The research also explored the use of aerogels in clothing as a novel nano-insulating material. The findings revealed that the weight and thickness of fire protective clothing using silica aerogel composite were reduced by over 70% while maintaining similar thermal protective performance.
Commercial applications in textiles
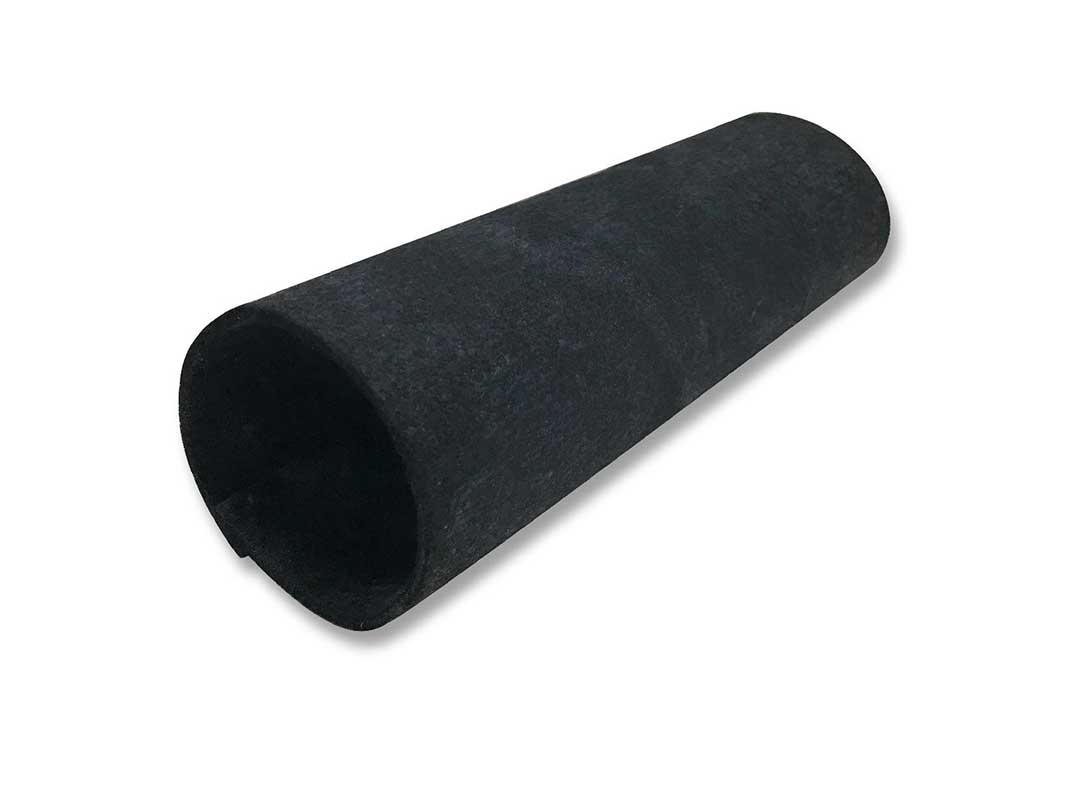
Most aerogel insulations take the form of a silica aerogel coated into or onto a substrate, such as a non-woven. Aerogel particles or granules are incorporated into nonwoven fabric structures using needle punching, thermal bonding, or resin bonding. Liquid silica aerogel precursor is applied to fabric through dip-coating, spray-coating, or plasma deposition. For possible textile applications, a carbon fibre-reinforced composite material manufactured from oxidized polyacrylonitrile fibers and SiO2 aerogel is available in the form of 1-3 mm thick sheets. Other examples include ceramic fiber aerogel blankets and aerogel insulation paper in varying thicknesses.

Conclusion
Aerogels possess excellent properties such as high heat insulation, flame resistance, water repellency, and sound insulation at an extremely low weight. These materials have been conventionally used for noise reduction and thermal insulation in a wide range of situations including cold & hot pipelines (petrochemical, foundry, chemical equipment), energy efficient buildings (floors, walls & ceilings), tanks, industrial furnaces, aerospace & defence, transportation (rail, ships and aircrafts), household appliances & cold storage, etc. Moreover, with technological advancements it is now possible to use aerogels for apparel or protective garment applications. For widespread adoption of this wonderful material in the protective workwear segment challenges such as high thickness & the associated bulkiness and rigidity, in addition to their higher pricing, need to be overcome. With growing commercial demand and the resultant economies of scale, these issues are expected to be resolved in the near future.


Leave a Reply